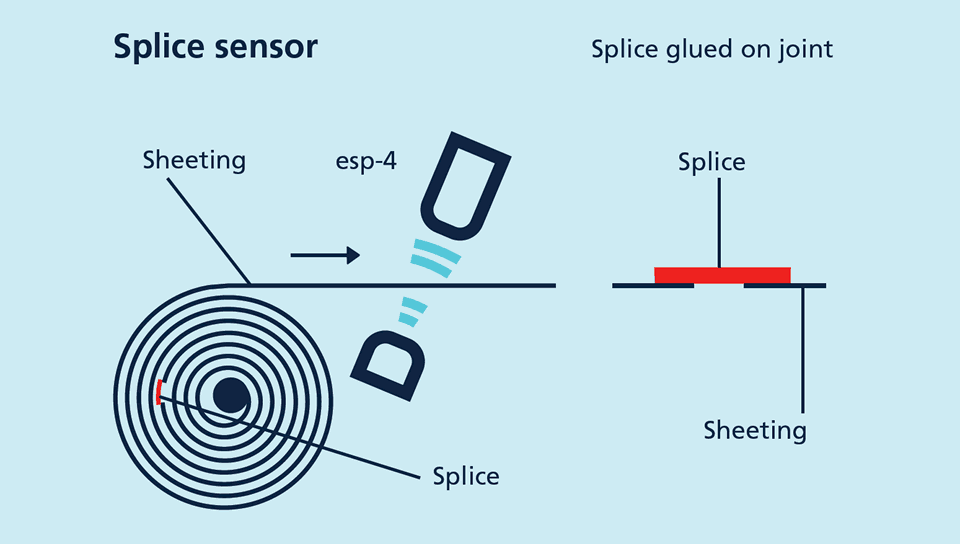
esp-4 – one unit for all cases:
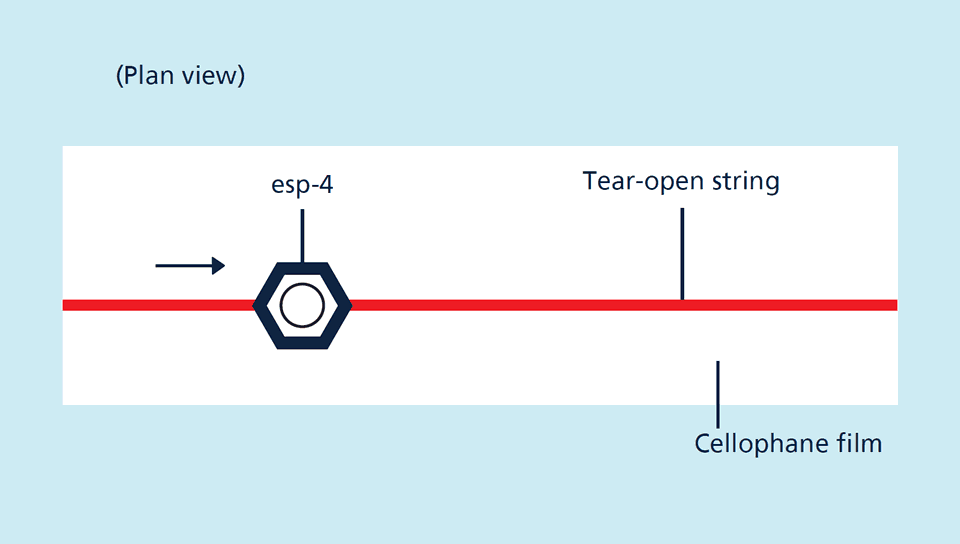
Label and splice sensor in one appliance
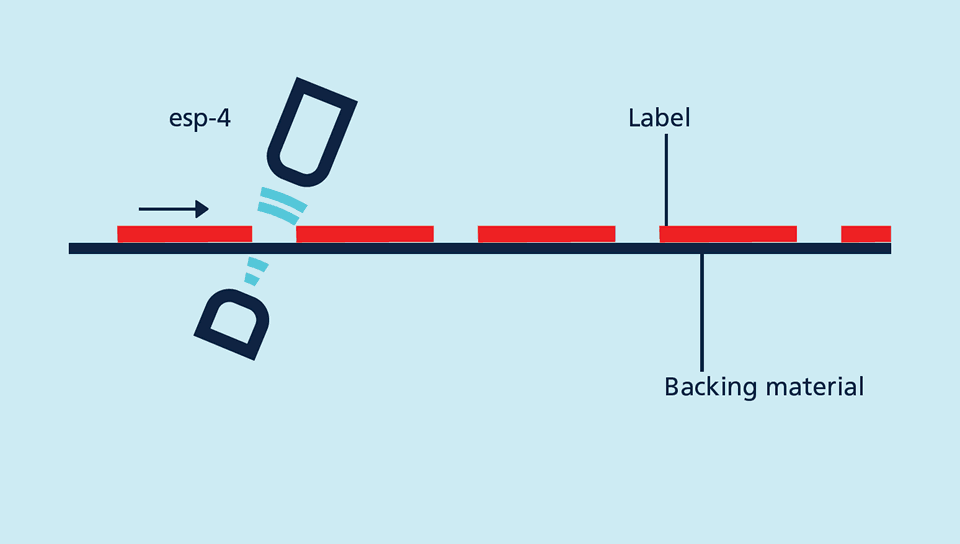
With a rapid pulse sequence, an ultrasonic transmitter beams upwards against the backing material. The effect of the sound pulses inducing the backing material to vibrate is for a markedly weakened sonic wave to be emitted on the opposite side.
The receiver receives this sonic wave and analyses it. The backing material signal level is different to that of the label or splice. And this difference in signal is analysed by the esp-4. The difference between backing material and a label or between sheeting and splice can be very slight indeed. In order to differentiate, the esp-4 sensor has to learn the signal level for the backing material or sheeting.
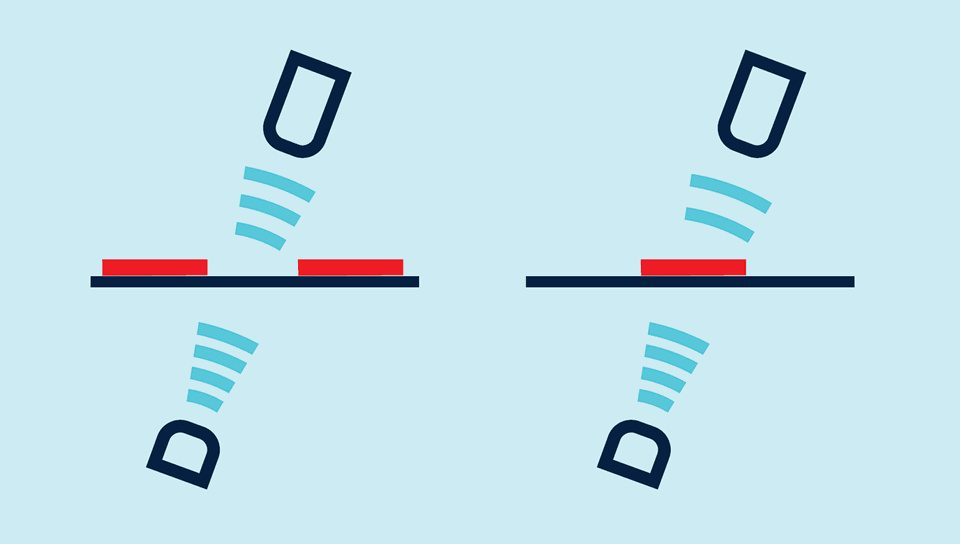
Backing material with label provides an attenuated signal level
The esp-4 sensors can be used as a label and splice sensor. The 3 Teach-in methods and QuickTeach allow the esp-4 sensor to be optimally set for each and every assignment.